Methods for Measuring Recent Temperatures
You learned that Earth’s global mean temperature (GMT) depends on a simple energy balance and that temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules composing a substance. There are several methods that can be used to determine temperature depending on how far back in time we want to examine.

Artists’ concept of National Polar-Orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System (NPOESS) satellite. Image Credit: NOAA
Earth’s global mean temperature (GMT) is determined by averaging measurements of air temperatures over land ocean surface temperatures. Thousands of weather stations spread over land surface worldwide measure the local air temperatures while thousands of ships and buoys measure the local sea surface temperatures. Surface temperature is measured not only by thermometers at ground-based weather stations and on ships, but also by satellites and weather balloons. These measurements are combined so that every square kilometer counts equally toward the global mean temperature.
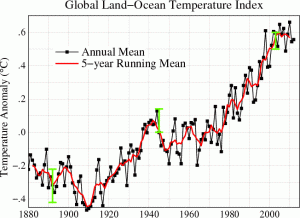
Temperature trends over time are often shown as temperature anomalies. A temperature anomaly is a departure from the long-term average. A positive temperature anomaly means that the temperature was warmer than the long-term average, and a negative temperature anomaly means that the temperature was cooler than the long-term average. Temperature anomalies are useful in analyzing trends.
Thermometer records have been kept for the past 150 years over much of Earth. By averaging these records, it is possible to estimate global mean temperature back to the mid-19th century.